 According to Mastercard, the payments giant has launched non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that grant access to the Mastercard Artist Accelerator program, designed to support emerging musicians. Developed in collaboration with Polygon, the NFT project highlights Mastercard’s intent to embrace Web3 technologies. Mastercard Launches Second NFT Offering In January, Mastercard announced its partnership with Polygon to support […]
According to Mastercard, the payments giant has launched non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that grant access to the Mastercard Artist Accelerator program, designed to support emerging musicians. Developed in collaboration with Polygon, the NFT project highlights Mastercard’s intent to embrace Web3 technologies. Mastercard Launches Second NFT Offering In January, Mastercard announced its partnership with Polygon to support […] A Layer two (L2) project, called Cryptogpt, which leverages ZK-rollup technology and artificial intelligence (AI), has announced that its team has raised $10 million in capital from a Series A funding round. The crypto and AI firm disclosed that the new funds would be used to expand into the largest Asian markets, and the company […]
A Layer two (L2) project, called Cryptogpt, which leverages ZK-rollup technology and artificial intelligence (AI), has announced that its team has raised $10 million in capital from a Series A funding round. The crypto and AI firm disclosed that the new funds would be used to expand into the largest Asian markets, and the company […] Economist Peter Schiff praised the artificial intelligence of the Chatgpt assistant for omitting bitcoin in a suggested “recession-proof” portfolio. The long-time gold proponent commented on a report claiming the chatbot has recommended “massive allocations” in precious metals. Schiff Cites Study Alleging Chatgpt Favors Gold and Cash as Investments in Recession Rigorous crypto opponent Peter Schiff […]
Economist Peter Schiff praised the artificial intelligence of the Chatgpt assistant for omitting bitcoin in a suggested “recession-proof” portfolio. The long-time gold proponent commented on a report claiming the chatbot has recommended “massive allocations” in precious metals. Schiff Cites Study Alleging Chatgpt Favors Gold and Cash as Investments in Recession Rigorous crypto opponent Peter Schiff […]
Discover how artificial intelligence is transforming the financial sector with nine examples of AI in finance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the financial sector, revolutionizing how banks, financial institutions and investors operate. Here are nine examples of AI in finance, and how they are changing the industry:
AI algorithms can analyze transactions in real time, detect anomalies and patterns that may indicate fraudulent activities, and alert banks to take appropriate actions. An example of fraud detection using AI is PayPal’s fraud detection system. PayPal uses machine learning algorithms and rule-based systems to monitor real-time transactions, and identify potentially fraudulent activities.
The system examines data points like the user’s location, transaction history, and device information to identify abnormalities and patterns that can hint at fraudulent behavior. The technology can notify PayPal’s fraud investigation team about a possibly fraudulent transaction so that they can look into it further or block the transaction. The amount of fraudulent transactions on the network has dramatically decreased thanks to this AI-powered solution, making using PayPal safer and more secure.
AI-powered chatbots can provide personalized financial advice, answer customer queries, and automate routine tasks like opening new accounts or updating customer information.
The chatbot “KAI” from Mastercard, which helps clients with account queries, transaction histories and expenditure tracking, is an example of how AI is being used in customer support. KAI uses machine learning algorithms and natural language processing to offer consumers tailored help and financial insights across a variety of channels, including SMS, WhatsApp, and Messenger.
brandchannel: Mastercard Grows Its Brand with New Personal Finance Chatbot KAI https://t.co/Mz3vPoDSJm pic.twitter.com/1zizdGgUac
— Muzaffaruddin Alvi (@Muzaffar69) October 25, 2016
AI can accurately assess past and present market trends, spot patterns, and predict future prices. AI algorithms can also perform transactions in real time, using pre-programmed rules and conditions, optimizing investing strategies and maximizing returns.
Financial institutions and investors benefit significantly from this technology, which enables them to make data-driven decisions and maintain an advantage in the fiercely competitive world of trading.
Related: What are artificial intelligence (AI) crypto coins, and how do they work?
By analyzing complex financial data, artificial intelligence can identify potential risks and forecast future scenarios, providing valuable insights that enable banks and other financial institutions to make well-informed decisions.
An example of risk management using AI is BlackRock’s Aladdin platform. To analyze enormous volumes of financial data, spot risks and opportunities, and give investment managers real-time insights, the Aladdin platform combines AI and machine learning algorithms.
Meet BlackRock’s all-knowing AI, ALLADIN. pic.twitter.com/EBDkaODzHl
— Hum₿le Warrior ⚔️ (@HumbleBitcoiner) August 11, 2022
By examining elements like market volatility, credit risk, and liquidity risk, the platform assists investment managers in monitoring and managing risks. Investment managers may enhance their investment strategies and make data-driven decisions thanks to Aladdin’s risk management capabilities, which lower the risk of losses and boost returns.
AI can analyze vast amounts of financial data and provide insights into investment trends, risks and opportunities, helping investors make informed decisions. An example of portfolio management using AI is Wealthfront, a robo-advisor that uses AI algorithms to manage investment portfolios for clients.
To create customized investment portfolios for clients based on their goals, risk tolerance, and financial position, Wealthfront combines classic portfolio theory and AI. As market conditions and the client’s goals change, the platform automatically rebalances the portfolio while continuously monitoring its performance. Many investors find Wealthfront an appealing alternative because of its AI-powered portfolio management, which enables customized and optimal investing plans.
AI algorithms can analyze credit histories, financial statements, and other data to provide accurate credit scores, enabling lenders to make better lending decisions. For instance, ZestFinance’s Zest Automated Machine Learning (ZAML) platform uses AI to analyze credit risk factors and provide more accurate credit scores, improving lending decisions and reducing the risk of default.
AI-powered robo-advisors can provide personalized financial advice and investment strategies based on a client’s financial situation, goals and risk tolerance. For instance, Bank of America’s AI chatbot, Erica, can provide personalized financial advice, answer customer queries and automate routine tasks.
The financial arena is an excellent fit for chatbots and other AI applications. One example: Bank of America’s Erica, a chatbot that provides customer service online by responding to basic inquiries. https://t.co/1uKslUKVJW #nuanceteam pic.twitter.com/U2iyxQHLv2
— Sebastien Le Corff (@twittseblec) April 25, 2018
AI can analyze a range of data points, including demographic information, health records and driving history, to provide accurate insurance underwriting. For instance, to improve accuracy and lower fraud in the insurance market, Lemonade, an AI-powered insurtech company, employs AI algorithms to evaluate claims and underwrite insurance policies.
Related: A brief history of artificial intelligence
AI can help financial institutions comply with complex regulations by analyzing transactions, detecting fraud, and ensuring compliance with Know Your Customer and Anti-Money Laundering regulations.
For instance, ComplyAdvantage helps businesses comply with legal obligations and avoid fines by using AI and machine learning algorithms to monitor financial transactions and identify potential money laundering activities.

An expert in the field of artificial intelligence is issuing a dire warning on the future of the rapidly-developing technology. In a new piece written for Time Magazine, AI research pioneer Eliezer Yudkowsky says the methods and structures currently used to grow AI are placing humanity in serious danger. Yudkowsky points to an open letter […]
The post Everyone on Earth Will Die Unless Major AI Changes Are Implemented, Warns Artificial Intelligence Expert appeared first on The Daily Hodl.

The scheme allegedly claimed it could generate returns of up to 2.2% a day by leveraging AI to trade more often and with higher profits than a person could.
Securities regulators from Montana, Texas, and Alabama have jointly filed enforcement actions against cryptocurrency trading platform YieldTrust.ai, alleging it is “perpetrating a Ponzi scheme.”
According to April 4 statements from the Montanan, Texan and Alabamian regulators, YieldTrust.ai and its Romanian owner, Stefan Ciopraga, claimed the decentralized application (DApp) called “YieldBot” is “powered by cutting-edge artificial intelligence” and is “capable of executing 70 times more trades with 25 times higher profits than any human trader could.”
The regulators alleged YieldTrust didn’t provide “any proof” to investors that the artificial intelligence (AI)-powered bot exists, “let alone that it is performing at the level YieldTrust.ai claims.”
Montana’s regulator stated in its cease and desist order that YieldBot was developed for Binance’s BNB Smart Chain and could interface with staking programs to generate returns for new investors of up to 2.2% per day through:
“[Analyzing] the crypto markets and – in milliseconds – make its own trading decisions, autonomously choosing from hundreds of trading methods and chaining them together to create unique strategies – achieving an exhilarating performance.”
However, the state regulators claimed an independent firm that conducted an audit of YieldBot’s smart contract found it was “dangerous,” as “the deploying team retained sufficient control to block users from withdrawing their assets.”
As noted by the regulator's statements and highlighted in an April 4 tweet from Montana’s securities commissioner, Troy Downing, scammers are apparently capitalizing on the hype surrounding AI “by developing high-tech ploys to deceive investors.”
Artificial intelligence may be an exciting concept, but scammers are attempting to capitalize on the excitement by developing high-tech ploys to deceive investors.#AI #SecuritiesFraud #InvestmentScam #MTNews https://t.co/FMSqLJW40E
— Commissioner Troy Downing (@DowningCSIMT) April 4, 2023
An order from Montana’s regulator demands YieldTrust.ai cease and desist all activity in the state and seeks a total of $100,000 in fines while the Texas State Securities Board issued multiple cease and desist orders.
Related: Bloomberg reveals AI for financial data, community responds
After the audit of its smart contract was published, YieldTrust.ai allegedly announced it would cease operations, which appears to be verified by the lack of trading activity according to DappRadar data.

However, the regulator’s orders accuse YieldTrust.ai of “raising capital from the public to cover withdrawals from prior investors,” which, alongside the promise of high returns, are the characteristics of a Ponzi scheme.
YieldTrust.ai’s website has been taken offline and its Twitter account deleted. Cointelegraph was unable to contact YieldTrust.ai or Ciopraga for comment.
AI has become far more prominent, accessible and surrounded by hype since the release of the ChatGPT AI chatbot on Nov. 30 by AI research company OpenAI.
Despite its inaccuracy at times, ChatGPT has proved to be a powerful tool, with the latest version capable of passing the bar, acing SATs and even identifying exploits in smart contracts.
Hodler’s Digest: FTX EU opens withdrawal, Elon Musk calls for AI halt, and Binance news
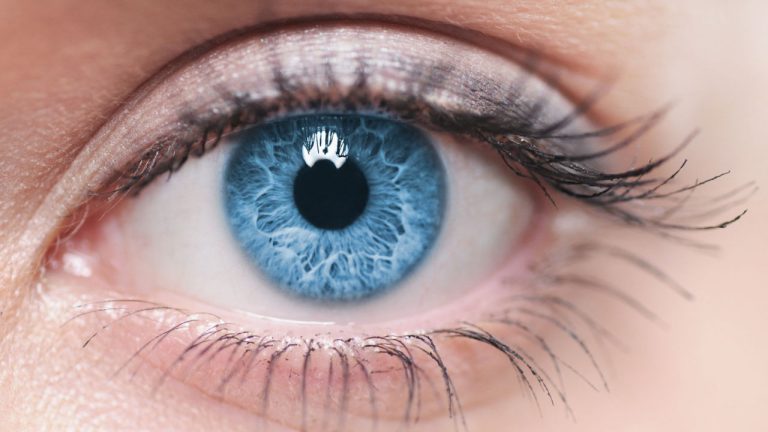 Worldcoin, a project co-founded by Sam Altman, who is also a co-founder of artificial intelligence (AI) startup Openai, announced the launch of World ID, a digital proof of personhood ID protocol. The protocol allows for an AI-resistant verification of humanness online, using a device called the orb to scan the iris of each person for […]
Worldcoin, a project co-founded by Sam Altman, who is also a co-founder of artificial intelligence (AI) startup Openai, announced the launch of World ID, a digital proof of personhood ID protocol. The protocol allows for an AI-resistant verification of humanness online, using a device called the orb to scan the iris of each person for […]
Michael Miller said generative AI is a move by digital companies to take the creative content of others "without remunerating them for their original work."
The creators of artificial intelligence (AI) fuelled applications should pay for the news and content being used to improve their products, according to the CEO of News Corp Australia.
In an April 2 editorial in The Australian, Michael Miller called for “creators of original journalism and content” to avoid the past mistakes that “decimated their industries” by allowing tech companies to profit from using their stories and information without compensation.
Chatbots are software that ingests news, data and other information to produce responses to queries that mimic written or spoken human speech, the most notable of which is the ChatGPT-4 chatbot by AI firm OpenAI.
According to Miller, the rapid rise of generative AI represents another move by powerful digital companies to develop “a new pot of gold to maximize revenues and profit by taking the creative content of others without remunerating them for their original work.”
Using OpenAI as an example, Miller claimed the company “quickly established a business” worth $30 billion by “using the others’ original content and creativity without remuneration and attribution."
The Australian federal government implemented the News Media Bargaining Code in 2021, which obliges tech platforms in Australia to pay news publishers for the news content made available or linked on their platforms.
Miller says similar laws are needed for AI, so that all content creators are appropriately compensated for their work.
“Creators deserve to be rewarded for their original work being used by AI engines which are raiding the style and tone of not only journalists but (to name a few) musicians, authors, poets, historians, painters, filmmakers and photographers.”
More than 2,600 tech leaders and researchers recently signed an open letter urging a temporary pause on further artificial intelligence (AI) development, fearing “profound risks to society and humanity.”
Meanwhile, Italy’s watchdog in charge of data protection announced a temporary block of ChatGPT and opened an investigation over suspected breaches of data privacy rules.
Miller believes content creators and AI companies can both benefit from an agreement, rather than outright blocks or bans on the tech.
I respect the concerns but am not gonna sign this. LLMs won't become AGIs. They do pose societal risks, as do many things. They also have great potential for good. Social pressure for slowing R&D should be reserved for bioweapons and nukes etc. not complex cases like this.
— Ben Goertzel (@bengoertzel) March 29, 2023
He wrote that with “appropriate guardrails,” AI has the potential to become a valuable journalistic resource. It can assist in creating content, “gather facts faster,” help to publish on multiple platforms and could accelerate video production.
Related: ‘Biased, deceptive’: Center for AI accuses ChatGPT creator of violating trade laws
The crypto industry is also starting to see more projects using AI, though it is still in the early stages.
Miller believes AI engines face a risk to their future success if they can’t convince the public that their information is trustworthy and credible, adding that “to achieve this they will have to fairly compensate those who provide the substance for their success."
Magazine: All rise for the robot judge: AI and blockchain could transform the courtroom

AI has evolved from the Turing machine to modern deep learning and natural language processing applications.
Multiple factors have driven the development of artificial intelligence (AI) over the years. The ability to swiftly and effectively collect and analyze enormous amounts of data has been made possible by computing technology advancements, which have been a significant contributing factor.
Another factor is the demand for automated systems that can complete activities that are too risky, challenging or time-consuming for humans. Also, there are now more opportunities for AI to solve real-world issues, thanks to the development of the internet and the accessibility of enormous amounts of digital data.
Moreover, societal and cultural issues have influenced AI. For instance, discussions concerning the ethics and the ramifications of AI have arisen in response to worries about job losses and automation.
Concerns have also been raised about the possibility of AI being employed for evil intent, such as malicious cyberattacks or disinformation campaigns. As a result, many researchers and decision-makers are attempting to ensure that AI is created and applied ethically and responsibly.
After +1000 tech workers urged pause in the training of the most powerful #AI systems, @UNESCO calls on countries to immediately implement its Recommendation on the Ethics of AI - the 1st global framework of this kind & adopted by 193 Member Stateshttps://t.co/BbA00ecihO pic.twitter.com/GowBq0jKbi
— Eliot Minchenberg (@E_Minchenberg) March 30, 2023
AI has come a long way since its inception in the mid-20th century. Here’s a brief history of artificial intelligence.
The origins of artificial intelligence may be dated to the middle of the 20th century, when computer scientists started to create algorithms and software that could carry out tasks that ordinarily need human intelligence, like problem-solving, pattern recognition and judgment.
One of the earliest pioneers of AI was Alan Turing, who proposed the concept of a machine that could simulate any human intelligence task, which is now known as the Turing Test.

Related: Top 10 most famous computer programmers of all time
The 1956 Dartmouth conference gathered academics from various professions to examine the prospect of constructing robots that can “think.” The conference officially introduced the field of artificial intelligence. During this time, rule-based systems and symbolic thinking were the main topics of AI study.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the focus of AI research shifted to developing expert systems designed to mimic the decisions made by human specialists in specific fields. These methods were frequently employed in industries such as engineering, finance and medicine.
However, when the drawbacks of rule-based systems became evident in the 1980s, AI research began to focus on machine learning, which is a branch of the discipline that employs statistical methods to let computers learn from data. As a result, neural networks were created and modeled after the human brain’s structure and operation.
AI research made substantial strides in the 1990s in robotics, computer vision and natural language processing. In the early 2000s, advances in speech recognition, image recognition and natural language processing were made possible by the advent of deep learning — a branch of machine learning that uses deep neural networks.
The first neural language model, that's Yoshua Bengio, one of the "Godfathers of Deep Learning"! He is widely regarded as one of the most impactful people in natural language processing and unsupervised learning.
— Damien Benveniste (@DamiBenveniste) March 27, 2023
Learn something new in https://t.co/8mUYA31M9R… pic.twitter.com/4f2DUE5awF
Virtual assistants, self-driving cars, medical diagnostics and financial analysis are just a few of the modern-day uses for AI. Artificial intelligence is developing quickly, with researchers looking at novel ideas like reinforcement learning, quantum computing and neuromorphic computing.
Another important trend in modern-day AI is the shift toward more human-like interactions, with voice assistants like Siri and Alexa leading the way. Natural language processing has also made significant progress, enabling machines to understand and respond to human speech with increasing accuracy. ChatGPT — a large language model trained by OpenAI, based on the GPT-3.5 architecture — is an example of the “talk of the town” AI that can understand natural language and generate human-like responses to a wide range of queries and prompts.
Related: Biased, deceptive’: Center for AI accuses ChatGPT creator of violating trade laws
Looking to the future, AI is likely to play an increasingly important role in solving some of the biggest challenges facing society, such as climate change, healthcare and cybersecurity. However, there are concerns about AI’s ethical and social implications, particularly as the technology becomes more advanced and autonomous.
Ethics in AI should be taught in every school.
— Julien Barbier ❤️☠️ 七転び八起き (@julienbarbier42) March 30, 2023
Moreover, as AI continues to evolve, it will likely profoundly impact virtually every aspect of our lives, from how we work and communicate, to how we learn and make decisions.
 This week, 2,600 tech industry moguls and entrepreneurs, including Elon Musk, Gary Marcus, and Steve Wozniak, signed an open letter requesting artificial intelligence (AI) labs to pause research and development for six months. The signatories believe that safety programs and regulations need to be strengthened, as they assert that AI labs are currently in an […]
This week, 2,600 tech industry moguls and entrepreneurs, including Elon Musk, Gary Marcus, and Steve Wozniak, signed an open letter requesting artificial intelligence (AI) labs to pause research and development for six months. The signatories believe that safety programs and regulations need to be strengthened, as they assert that AI labs are currently in an […]