
The UK Treasury has amended finance laws to clarify that crypto staking isn’t a collective investment scheme, which a lawyer says is “heavily regulated.”
The UK Treasury has amended a law clarifying that crypto staking — necessary for proof-of-stake blockchains such as Ethereum and Solana — doesn’t fall under the definition of a “collective investment scheme,” which is typically heavily regulated.
A Jan. 8 order from the department amends a section of The Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 about group investments, adding that “arrangements for qualifying cryptoasset staking do not amount to a collective investment scheme [CIS].”
It clarifies that “qualifying cryptoasset staking” means validating transactions on a blockchain, a distributed ledger technology network “or other similar technology.”
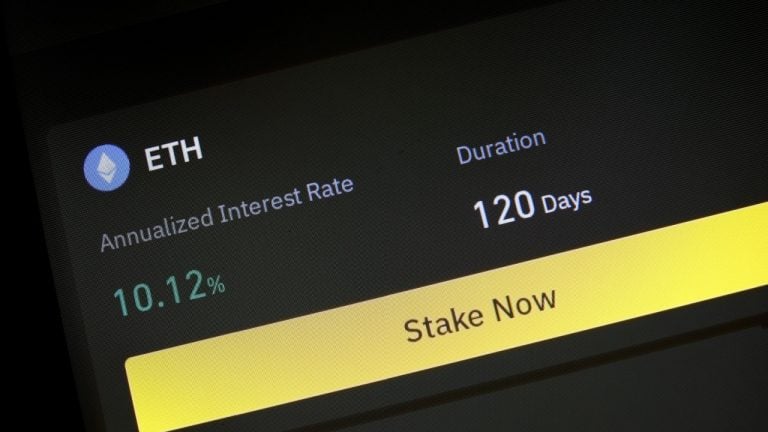 In the first quarter of 2024, approximately $43.8 billion, or 76% of the decentralized finance yield market, earned an annual percentage yield (APY) of about 5% in very low-risk contracts. Staking played a crucial role in the resurgence of decentralized finance, bolstered by the Ethereum network’s transition to a Proof-of-Stake model. The bridging sector experienced […]
In the first quarter of 2024, approximately $43.8 billion, or 76% of the decentralized finance yield market, earned an annual percentage yield (APY) of about 5% in very low-risk contracts. Staking played a crucial role in the resurgence of decentralized finance, bolstered by the Ethereum network’s transition to a Proof-of-Stake model. The bridging sector experienced […]
This article provides a deep dive into leased proof-of-stake (LPoS), establishing how it works, its benefits, key features and its role in blockchains.
LPoS is a type of PoS meant to increase mining power, address inherent issues found in PoW, and improve other types of PoS, such as delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS).
Regular cryptocurrency users have probably come across the term proof-of-stake (PoS) when dealing with crypto staking, but what is leased proof-of-stake (LPoS), and is there a connection between the two?
Yes, they are related, as LPoS is simply a variant of the PoS system. Proof-of-stake is a key element of the blockchain consensus mechanism, where validators participate in staking to generate and validate transaction blocks.
Validators on proof-of-stake platforms typically have to stake more cryptocurrency to improve their chances of block generation, and here is where LPoS comes in handy. Tokenholders who don’t have the technical know-how or financial muscle can lease their tokens to validator node operators, enhancing the validator’s chance to receive the opportunity to create new blocks. In return, they will earn a share of the transaction fee paid to the validator.
In an LPoS environment, tokenholders can lease their stake or run a full node. However, the more tokens staked by a node, the better its chances of being selected to generate a new block. LPoS allows users to acquire the proceeds of mining without going through the mining process.
LPoS operates on the same premises as a lottery in that more stakes increase someone’s chances of winning rewards.
So, how does leased proof of stake work? The LPoS system follows a series of set processes:
Please note that the leased tokens never actually leave the leaser’s hardware wallet and remain in total control of the tokenholder. The holder only links the chosen node(s) and doesn’t transfer the tokens to the said node.
No party can trade or transfer the tokens, including the holder. The holder can only transact or spend the allotted coins upon canceling the lease.
Some of the features of LPoS include decentralization, balance leasing, fixed tokens and scalability.
The main features of LPoS include:
Leased tokens do not transfer to validators, nor can they be traded. Users can lease out their tokens and money from cold storage or wallets.
LPoS divides rewards based on the staked amount, doing away with the need for a mining pool. It’s also great for blockchain governance, as it uses a peer-to-peer protocol to prevent third-party intervention.
There’s no way to predict who will win the right to generate the next block. The only thing worth noting is that the bigger a node’s economic stake, the greater its chances of winning the right to generate the next block.
Mining does not add more tokens to LPoS, as the system only allows token leasing.
Developers of LPoS prioritize high-on-chain scalability over second-tier apps.
Other blockchain systems offer block token rewards, but LPoS issues transaction fees to reward successful node operators.
LPoS is a type of PoS used to validate cryptocurrency transactions in a blockchain network.
LPoS utilizes nodes or network devices to verify and validate blockchain transactions. Node-based validation uses computational randomness, hinged on the financial stake of a node, to assign rights to validate blockchain transactions.
A PoS consensus algorithm relies on these factors to determine what node is best fit to validate transactions at any given time:
PoS uses passive cryptocurrency deposits rather than the raw computational power in mining hardware used in proof-of-work (PoW) systems, making PoS more resource-efficient than PoW.
Currently, two leading blockchains use LPoS. The first is the Waves blockchain, which uses the LPoS consensus algorithm to verify the blockchain’s state by allowing users to lease tokens to generating nodes and receive rewards distributed by these nodes. Finally, Nix utilizes a permissionless staking mechanism that allows users to stake through a different third-party wallet, with the third party responsible for the staking.

The many benefits of LPoS stem from gaining rewards without actively trading, increasing your chances of receiving rewards by joining a larger node, and the inherent security features hard-baked into the LPoS process.
One can realize several benefits from engaging in LPoS:
Users can participate in block generation and receive some rewards without actually participating in the block-generating process.
LPoS protocols contain a minimum investment requirement for network participation. For instance, Waves only allows a node to participate in block generation if it has a minimum of 1,000 Waves (WAVES). Investors with less than this can lease cryptocurrency tokens to more prominent nodes for a chance at gaining rewards.
The LPoS generating balance rule calculates the lowest balance after considering leasing in the latest 1,000 blocks, thwarting manipulation attempts by moving funds between accounts.
The LPoS works in a way that rewards nodes with the most significant economic stake in the network. Therefore, leasing tokens to a bigger node increases the chances of receiving rewards than if the leaser decided to go solo.
No one can trade or transfer the leased tokens (which won’t even leave the wallet), minimizing the chances of loss.
It does not require mining hardware to participate in validation.
Alternatives to LPoS that utilize PoS include delegated proof-of-stake, pure proof-of-stake and proof-of-validation.
While technically not a way to mine cryptocurrencies, PoS allows users to validate transactions and create new blocks on a blockchain. LPoS enables users to lease crypto tokens to nodes that validate LPoS transactions.
Several alternatives to LPoS allow users to make use of the PoS consensus mechanism:
Users can delegate the production of new blocks to delegates or witnesses through a democratic voting system, with votes weighted by the number of tokens held on a platform.
This one is mainly used by the Algorand blockchain for the development of decentralized applications (DApps). Users can cast their votes to select representatives who vote on proposals and propose new blocks.
This aims to achieve consensus through staked validator nodes. The number of tokens staked with each validator determines the validator’s voting numbers. When a validator with a minimum of two-thirds of the network’s total voting submits a commit vote on a block, that validates the new block.
Some LPoS protocols leverage the power of PoS and PoW. They use PoW to create new block housing transactions and use PoS to validate the blocks.

Mihailo Bjelic suggested that adding zero-knowledge proof technology could bolster the network’s security while still keeping fees low.
Polygon co-founder Mihailo Bjelic has proposed upgrading the Polygon Proof of Stake (PoS) network to a “zkEVM validium” version, according to a June 20 forum post. If the upgrade is implemented, the new version will rely on zero-knowledge proofs to increase security.
HUGE UPDATE ON #Polygon
— Hitesh Malviya (@hmalviya9) June 20, 2023
Polygon may go through some huge changes in near future. @MihailoBjelic shared a polygon improvement proposal few hours ago which discussed to upgrade polygon POS to zkEVM Validium.
According to the proposal, Polygon POS is facing three key challenges…
Polygon PoS is an Ethereum scaling solution that has over $900 million total value locked within its contracts and does over 2 million transactions per day. It was first launched in 2019. In March, the Polygon team launched a second network, Polygon zkEVM, that uses zero-knowledge proof rollups to scale Ethereum.
In the June 20 post, Bjelic proposed to also upgrade the old PoS network to a zkEVM version, making both networks rely on zero-knowledge proofs. However, unlike the network that just launched in March, the new version of Polygon PoS will not be a “rollup,” Bjelic stated. In other words, it will not store compressed transaction data on Ethereum. Instead, it will be a “validium” that stores only validation proofs on layer 1, while the actual transaction data will be kept on a separate chain.
This compromise will allow Polygon PoS to have lower transaction fees than Polygon zkEVM. It will also increase the security of Polygon PoS, since it will allow the network to inherit Ethereum’s security, the co-founder concluded.
Related: Why ZK-rollups need data availability
Once the upgrade is implemented, Polygon zkEVM may be used for high-value transactions where security is of the utmost importance, whereas Polygon PoS may become the network for gaming and social media enthusiasts, Bjelic suggested, stating:
“Upgraded Polygon PoS (zkEVM validium) would offer very high scalability and very low fees, with the tradeoff of storing transaction data locally instead of on Ethereum. It would be a great fit for applications that have high transaction volume and require low transaction fees, e.g. Web3 gaming and social.”
The Polygon co-founder offered a timeline for when he thought the upgrade could be implemented, stating that his informal proposal could be turned into a formal Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP) by November and implemented on mainnet sometime between February and March, 2024.
The launch of Polygon zkEVM and upgrading of Polygon PoS is part of a grand plan by the team to create a “Supernet” uniting many different application-specific chains. The devs call this project “Polygon 2.0.”
The native coin of the Polygon ecosystem, called “MATIC,” was delisted by eToro on June 13 after the United States Securities and Exchange commission claimed that it had been sold as an unregistered security. The Polygon team has denied that their fundraise violated any U.S. laws.
 In the past 20 days, the Arbitrum blockchain has recorded a significant number of transactions coinciding with the recent ARB airdrop that occurred on March 23. About two weeks ago, on that day, the Arbitrum network recorded an all-time high of 2.72 million transactions settled in 24 hours. L2 Network Arbitrum Records 2.72 Million Transactions […]
In the past 20 days, the Arbitrum blockchain has recorded a significant number of transactions coinciding with the recent ARB airdrop that occurred on March 23. About two weeks ago, on that day, the Arbitrum network recorded an all-time high of 2.72 million transactions settled in 24 hours. L2 Network Arbitrum Records 2.72 Million Transactions […] In recent times, Bitcoin’s hashrate has been consistently above 300 exahash per second (EH/s) as multiple mining pools dedicate significant hashpower to the Bitcoin blockchain today. Interestingly, some of the world’s top bitcoin mining pools are also using their hashrate to merge-mine other coins, and these networks have benefited from bitcoin’s increased hashrate. How Bitcoin’s […]
In recent times, Bitcoin’s hashrate has been consistently above 300 exahash per second (EH/s) as multiple mining pools dedicate significant hashpower to the Bitcoin blockchain today. Interestingly, some of the world’s top bitcoin mining pools are also using their hashrate to merge-mine other coins, and these networks have benefited from bitcoin’s increased hashrate. How Bitcoin’s […] After the transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum’s annual issuance rate has been reduced to negative 0.057%, according to statistics 158 days after The Merge. The metrics indicate that more ethereum tokens have been removed than issued, and if the chain were still under PoW consensus, 1,823,678 ether would have been minted to […]
After the transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), Ethereum’s annual issuance rate has been reduced to negative 0.057%, according to statistics 158 days after The Merge. The metrics indicate that more ethereum tokens have been removed than issued, and if the chain were still under PoW consensus, 1,823,678 ether would have been minted to […]
A Nansen in December noted that Ether staking solutions had been in high demand since Ethereum’s shift to proof-of-stake.
Liquid staking protocol Lido Finance appears to have benefited most from the Ethereum merge in September, with its total value locked (TVL) now sitting at the top position among other decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols.
According to data from DeFiLlama, Lido’s liquid staking protocol now commands $5.9 billion in TVL, compared to MakerDAO's $5.89 billion and AAVE’s $3.7 billion.
Lido now has the highest TVL of any DeFi protocol. pic.twitter.com/2xsM3lVGVl
— Patrick | Dynamo DeFi (@Dynamo_Patrick) January 1, 2023
According to Lido Finance’s website, as at Jan. 2 had $5.8 billion Ether (ETH) staked. Meanwhile, there was around $23.2 million staked in Solana (SOL), $43.9 million in Polygon (MATIC), $11 million in Polkadot (DOT) and $2.2 million in Kusama (KSM).
Lido’s model allows users access to liquid Ether staking without committing to the traditional 32 ETH minimum.
Blockchain data analytics from Nansen in December noted that staking solutions such as these had been in high demand since Ethereum’s shift to proof-of-stake.
It’s report highlighted the impact of the Merge in introducing staked ETH as an out-and-out cryptocurrency-native yield-bearing instrument that has quickly outstripped other collateralized yield-bearing services.
Lido appears to have benefitted from this, as its fee revenue has been directly proportional to Ethereum Proof-of-stake (PoS) earnings since Lido sends received Ether to the staking protocol.
In Nov. 2022 that Lido said it has been collecting $1 million in fees every day since Oct. 2022.
Related: 5 altcoin projects that made a real difference in 2022
Meanwhile, the governing body of the Maker protocol MakerDAO saw its revenue decline to just over $4 million in Q3, a 86% plunge from the previous quarter according to a Messari statement in Sept. 2022, citing few liquidations and weak loan demand as the reasons for the decline.
In that same month, Lido held the most amount of staked ETH amongst DeFi, with 31% according to Nansen in September, which is a significant amount compared to major crypto exchanges Coinbase and Kraken, holding 15% and 8.5% respectively.
 Its been 105 days since Ethereum transitioned from a proof-of-work (PoW) blockchain to a proof-of-stake (PoS) network and the number of Ethereum validators is set to surpass 500,000 in 2023. According to metrics, Ethereum’s issuance rate of new coins has dropped considerably and only 4,790.45 ether has been minted since The Merge took place on […]
Its been 105 days since Ethereum transitioned from a proof-of-work (PoW) blockchain to a proof-of-stake (PoS) network and the number of Ethereum validators is set to surpass 500,000 in 2023. According to metrics, Ethereum’s issuance rate of new coins has dropped considerably and only 4,790.45 ether has been minted since The Merge took place on […]
Lido protocol boasts $1 million in daily fee revenue for nearly a month, highlighting its growth in daily active users and Ethereum stakers.
The crypto market has witnessed a turbulent few weeks after the FTX collapse but Lido Finance, a liquid staking protocol, has been a bright spot amidst the chaos. According to Data from DeFiLlama, Lido protocol has earned $1 million or more in fees daily since October 26.
Lido fees and revenue over time. Lido has collected over $1M in fees every day since October 26th pic.twitter.com/GHkzSzYIOo
— DefiLlama.com (@DefiLlama) November 18, 2022
Let’s analyze the on-chain fundamentals to see why this trend has continued.
Lido’s growth started in May 2021, pre-FTX collapse. The fees reached an all-time high on Nov. 10 as fee revenue nearly topped $2.6 million. The protocol earns 10% of the total Ethereum (ETH) staking rewards generated from user deposits.
Data also shows a steady increase in deposits to Ethereum’s PoS consensus translates to an uptick in Lido’s fee capture.

Lido’s fee revenue moves in tandem with Ethereum Proof-of-stake (PoS) earnings since Lido sends received Ether to the staking protocol. After the FTX collapse, Ethereum activity has grown thanks to an uptick in decentralized exchange (DEX) activity. Ethereum fees and revenue also reached a 30-day peak on Nov. 8, posting $9.1 million in fees and $7.3 million in revenue.

Unique depositors into the Lido protocol have reached 150,000, demonstrating that Lido is continuing to attract new users. The increase in unique deposits comes after centralized “earn” programs have shown weaknesses due to exposure to their exposure to FTX, Genesis, BlockFi and others.

Daily active users and Lido (LDO) token holders are also increasing on Lido. According to data from Token Terminal, daily active users hit a 90-day high of 837 on Nov. 17 further bolstering the platform’s positive momentum.

Related: DeFi platforms see profits amid FTX collapse and CEX exodus
While fees, deposits and revenue continue to increase for Lido, the market cap of LDO tokens is not keeping pace.
As mentioned above, Lido hit a record amount of fees on Nov. 10, at the same time the market cap decreased from $1.2 billion to $663.7 million.
According to Coingecko, during this same period, the price of LDO tokens dropped from $1.80 to a low of $0.90.

Despite the market-wide downturn, Lido is showing strong fundamentals on multiple fronts. The steady uptick in DAUs, revenue and new unique participants are all key components for assessing growth and sustainability within a DeFi platform.
The views and opinions expressed here are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Cointelegraph.com. Every investment and trading move involves risk, you should conduct your own research when making a decision.